- Home
- Plastic at Home
- Plastic Recycling Codes
- Mechanical Recycling
What is Mechanical Recycling, How It Works, and Its Advantages

Plastic. It's everywhere we look, from the water bottles we use daily to the packaging that protects our groceries. But what happens to all this plastic once we're done with it? Ideally, it gets recycled, but not all recycling is created equal.
Today, we're diving into the world of mechanical recycling – a method for giving plastic waste a new lease on life.
What is Mechanical Recycling?
Imagine taking a used plastic bottle and turning it into something new, like fleece jackets or even playground equipment. That's the basic idea behind mechanical recycling. In contrast to chemical recycling, mechanical recycling involves only mechanical processes (grinding, washing, separating, drying, re-granulating and compounding) to break down plastic waste into its basic building blocks without changing its chemical structure.
This process can be broken down into several distinct stages:
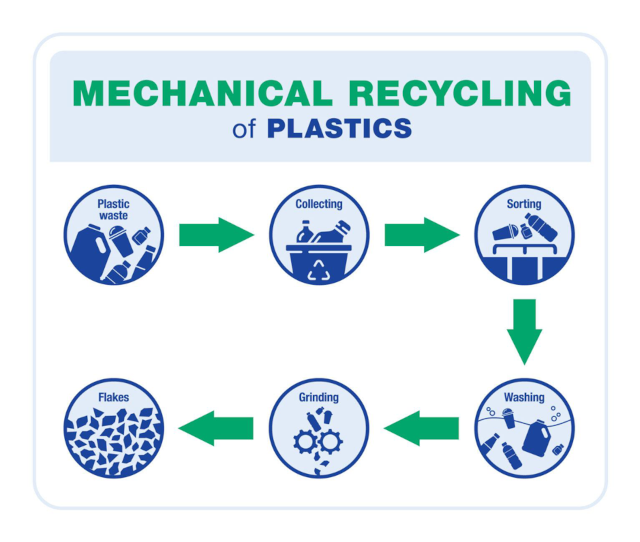 Photo: ©Drugplastics.com (https://www.drugplastics.com/an-introduction-to-advanced-plastic-recycling/amp/)
Photo: ©Drugplastics.com (https://www.drugplastics.com/an-introduction-to-advanced-plastic-recycling/amp/)1. Collection and Sorting
The initial phase involves the gathering of plastic waste from various sources, including households, industrial facilities, and commercial establishments. A critical first step necessitates the meticulous sorting of plastics into designated categories based on their unique resin identification codes. These codes function as a standardized classification system, guaranteeing compatibility throughout the subsequent stages of the process.
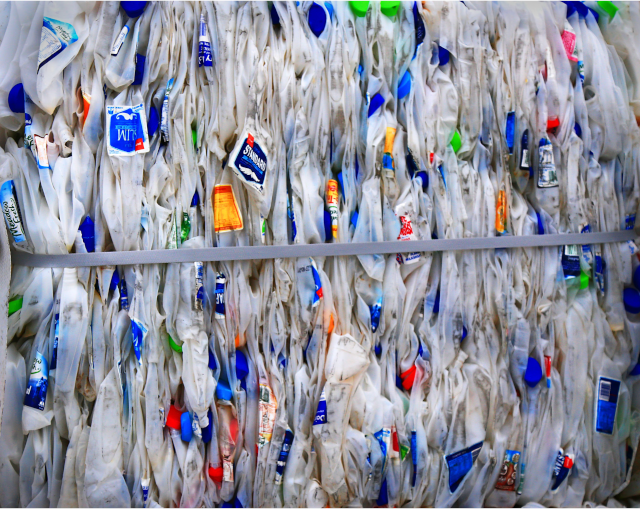

2. Cleaning
Following the sorting procedure, the plastics undergo a rigorous cleaning regimen to remove contaminants such as dirt, residual food particles, and any adhering labels. This meticulous cleaning step is paramount in ensuring the overall quality and purity of the recycled material.
3. shredding
The cleansed plastic undergoes a size reduction process, where it is shredded into smaller flakes or chips. This increases the surface area of the material, facilitating further processing in the subsequent stages.
4. Melting and Extrusion
This stage represents a pivotal transformation. The shredded plastic is subjected to elevated temperatures, reaching its melting point and transitioning into a molten state. This molten plastic is then forced through a specialized apparatus known as an extruder. This machinery operates similarly to a Play-Doh Fun Factory, shaping the molten plastic into uniform pellets or granules.
5. Quality Control
Just as with any manufactured product, the resulting plastic pellets undergo a rigorous quality inspection. This ensures that the pellets meet the requisite specifications for their intended use in the production of new plastic products.
6. Manufacturing
The final stage marks the culmination of the process. The high-quality recycled pellets are utilized as raw materials in the manufacturing of a diverse range of products, effectively granting plastic a second life. These products encompass a wide spectrum, including packaging containers, articles of clothing, and even components employed in the construction industry.

What are the advantages of mechanical recycling?
Mechanical recycling offers numerous advantages, making it a crucial component of sustainable waste management strategies. Some of the key benefits of mechanical recycling include:
1. Resource Conservation
By recycling plastic materials through mechanical processes, we can conserve valuable natural resources. Mechanical recycling reduces the demand for virgin plastics derived from fossil fuels, such as petroleum, thus helping to preserve finite resources and reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
2. Energy Savings
Compared to the production of virgin plastics, mechanical recycling consumes less energy. Processing recycled plastics requires lower energy inputs since the polymer chains are already formed. This results in reduced gas emissions and environmental impact associated with plastic manufacturing.
3. Waste Reduction
Mechanical recycling diverts plastic waste from landfills and incinerators, thereby reducing environmental pollution and alleviating the burden on waste management systems. By transforming plastic waste into reusable materials, mechanical recycling helps mitigate the negative environmental consequences of plastic pollution, such as marine debris and habitat destruction.

4. Economic Benefits
Recycling industries create jobs and stimulate economic growth by generating employment opportunities and fostering innovation. Mechanical recycling contributes to the development of a circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled in a closed-loop system, reducing the need for raw material extraction and waste disposal costs.
5. Closed-Loop Systems
Mechanical recycling enables the creation of closed-loop systems, where recycled materials are reintegrated into the production process to manufacture new products. This closed-loop approach reduces the environmental footprint of consumer goods and promotes circularity by minimizing waste generation and maximizing resource efficiency.
6. Consumer Demand and Corporate Responsibility
Increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and growing demand for sustainable products have led to greater adoption of mechanical recycling by businesses and manufacturers. Companies are embracing recycled materials in their products to meet consumer expectations for eco-friendly and socially responsible options, driving market demand for recycled plastics.
7. Versatility and Accessibility
Mechanical recycling is a versatile and accessible recycling method that can be implemented on a large scale. It can accommodate various types of plastics and is suitable for processing plastic waste collected from diverse sources, including households, industries, and commercial establishments. This accessibility makes mechanical recycling an integral part of municipal recycling programs and industrial waste management practices.
As we've seen, mechanical recycling offers a powerful solution for plastic waste management, transforming it into valuable resources. It conserves resources, reduces energy use, and diverts plastic from landfills, promoting a circular economy.
However, it's crucial to remember that recycling alone isn't the ultimate answer. The ideal scenario is to minimize plastic use altogether. By opting for reusable alternatives, choosing products with minimal packaging, and supporting companies committed to sustainable practices, we can significantly reduce our plastic footprint. While mechanical recycling remains a cornerstone of responsible plastic management for the foreseeable future, prioritizing plastic reduction is the key to a truly sustainable future.
Resources














